History of AI Tools: From Turing to Today
Published: 01 Jan 2025
What are AI tools?
You can use AI tools on your computer to do things that normally require human intelligence, like understanding words, recognising speech, or making decisions. These tools are useful in many areas of life, like work, medicine, and fun.
Definition: AI tools are technologies that help computers or machines think and act like humans.
- Examples:
- Siri or Google Assistant: Voice recognition tools in smartphones.
- Netflix Recommendations: AI helps suggest movies based on your preferences.
- Google Translate: AI that translates languages.
Why Understanding the Evolution of AI Tools is Important Knowing how AI tools have developed can help us predict what they might do in the future. It also helps us understand the challenges and opportunities AI presents.
- Understanding the Past: AI has come a long way from simple programs that played games like chess to powerful tools that assist with complex tasks.
- Looking Ahead: By knowing where AI started, we can imagine what might be possible in the future, like fully self-driving cars or smarter virtual assistants.
Preview: From Early Experiments to Today’s AI Innovations In the next sections, we’ll journey through the history of AI tools. We’ll look at how they started as simple experiments and how they’ve evolved into the powerful tools we use today.
1. The Dawn of AI (1950s–1970s)
The test checks to see if a person can tell the difference between a computer and a real person. The machine is said to “think” if it cannot tell the difference.
Why it’s important: Turing’s ideas sparked the idea that machines could one day think or act like humans, setting the stage for AI development.
First AI Programs:
Logic Theorist and ELIZA: Early AI Milestones
- Logic Theorist (1956):
- Developed by Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon.
- First AI program designed to mimic human problem-solving.
- Successfully proved mathematical theorems.
- ELIZA (1960s):
- Created by Joseph Weizenbaum.
- One of the first chatbots, mimicking human conversation.
- Used a script called DOCTOR to simulate a psychotherapist.
Example: How ELIZA Simulated Conversations Imagine chatting with a robot that asks you, “How are you feeling today?” and responds to your answers with thoughtful questions, just like a therapist would. That’s what ELIZA did. While simple, it showed that computers could process human language and engage in basic conversations. This was the beginning of AI tools that could understand and interact with people.
- 1950: Alan Turing proposes the Turing Test.
- 1956: The Logic Theorist is developed.
- 1960s: ELIZA chatbot is created.
- 1970s: AI research begins to expand with more specialized programs, but progress slows due to limited computing power.
This period laid the groundwork for AI, showing that machines could perform tasks that were once thought to require human intelligence.
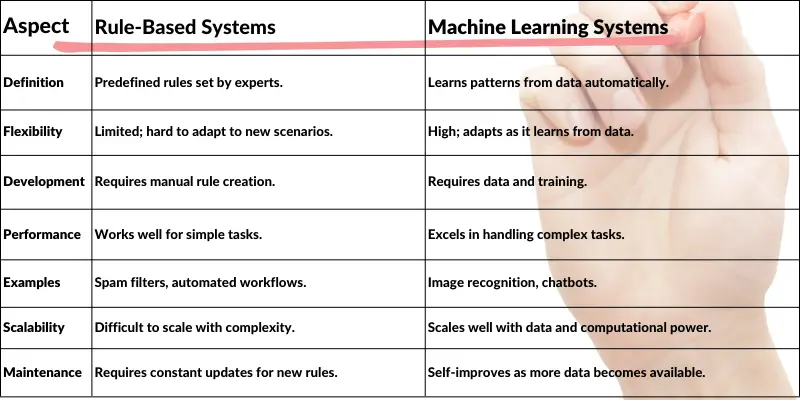
2. Rule-Based Systems and Expert Systems (1980s)
The Rise of Expert Systems: AI in Specialized Fields
- Expert Systems (1980s): AI programs designed to mimic human decision-making using predefined rules.
- MYCIN:
- Developed to help doctors diagnose bacterial infections.
- Analyzed symptoms and medical data to recommend antibiotics.
- Impact: Showed that AI could support expert-driven fields like healthcare by providing accurate, knowledge-based recommendations.
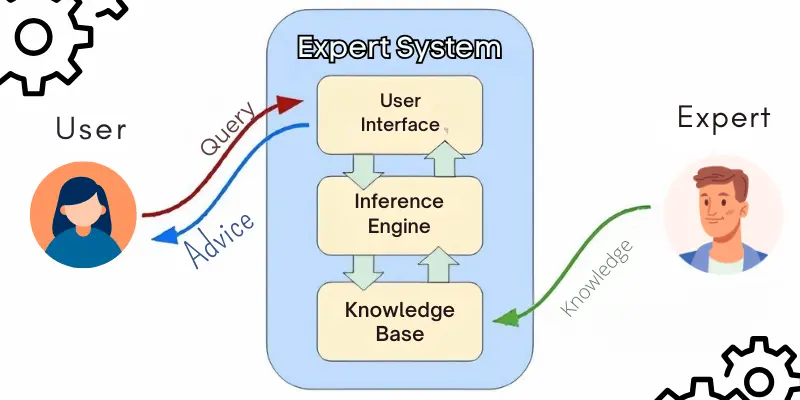
Limitations in AI Tool Development:
Challenges Faced by Rule-Based Systems Despite their promise, expert systems like MYCIN had limitations that slowed AI’s growth:
- Limited Flexibility: Expert systems worked only with the specific rules programmed into them. They couldn’t adapt to new situations or learn from experience.
- Dependency on Human Knowledge: They required experts to create and update rules, which limited them to the knowledge available at the time.
- High Maintenance: Any change in medical knowledge or new information required reprogramming the system, which was time-consuming.
These challenges made it clear that expert systems, while useful, weren’t as smart or flexible as human experts.
Example: How MYCIN Was Used in Diagnosing Bacterial Infections but Faced Limitations MYCIN was used by doctors to help diagnose bacterial infections based on a patient’s symptoms. It would ask questions like, “Does the patient have a fever?” or “What are the results of the blood test?” Based on the answers, MYCIN could suggest a diagnosis and recommend antibiotics.
However, MYCIN had limitations:
- It couldn’t handle complex cases where the rules didn’t fit perfectly.
- It couldn’t update itself with new medical research or adapt to new kinds of bacteria without human input.
- MYCIN was also limited in dealing with uncertainty, such as when a patient had multiple potential diagnoses.
| Trend: Early Skepticism About AI’s Potential and Growth in the Development of Artificial Intelligence Tools |
|---|
AI Challenges and Progress in the 1980s
|
3. The AI Winter (Late 1980s–1990s)
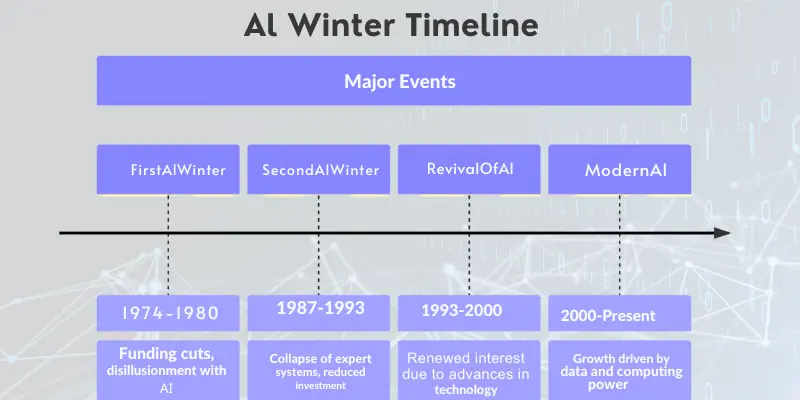
Why AI Progress Slowed:
During the late 1980s and 1990s, AI experienced a slowdown known as the AI Winter, where research progress was limited due to two main reasons:
- Unrealistic Expectations: Early hype led to exaggerated promises about AI’s rapid growth. When AI failed to meet these high expectations, interest declined.
- Lack of Funding: As AI progress slowed, governments and companies reduced funding, causing many projects to be delayed or abandoned.
Lessons Learned:
The AI Winter shaped the future of AI in several ways:
- Realistic Expectations: Researchers learned to set achievable goals, focusing on solving practical problems instead of aiming for overly ambitious breakthroughs.
- Clear Applications: AI needed well-defined real-world uses to attract funding, leading to its success in fields like finance, healthcare, and data analysis.
- Advances in Computing Power: While AI research slowed, improvements in computing technology laid the foundation for future AI growth.
These lessons helped AI evolve into a more practical and effective field, leading to the advancements we see today.e today.
4. The Rise of Machine Learning (2000s)
In the 2000s, AI shifted from rule-based systems to machine learning, which allowed computers to learn from data instead of following strict instructions.
- How It Works: Machine learning trains algorithms to recognize patterns in data. The more data they process, the better they become at making predictions or decisions.
- Why It Matters: As the internet expanded, vast amounts of data became available. Machine learning became essential for analyzing and understanding this data, driving AI advancements in various fields.
This shift made AI more flexible, powerful, and widely applicable.
Mainstream AI Applications:
By the 2000s, AI-driven tools began shaping user experiences through personalized recommendations and content customization:
- AI-Powered Recommendations: Amazon and Netflix used machine learning to suggest products and movies based on user behavior.
- Content Personalization: AI helped businesses tailor experiences to individual preferences.
- User Engagement: Personalized content made services more useful and increased customer satisfaction.
These examples highlight how AI-powered machine learning transformed digital experiences:
- Amazon: Tracks your purchases, searches, and viewed items to recommend products you might like. This makes shopping more personalized and efficient.
- Netflix: Analyzes your watch history to suggest movies and shows based on your preferences. The more you watch, the better the recommendations get.
These advancements demonstrated how AI tools could adapt to user behavior, improving convenience and engagement in everyday services.g, could make services smarter and more tailored to individual needs.
| Trend: Machine Learning Becoming the Foundation for Modern AI Tools |
|---|
|
Machine Learning: The Backbone of Modern AI Tools Machine learning has become the core technology behind many AI advancements, powering tools like:
As data continues to grow, machine learning models are becoming more accurate and efficient, shaping the future of AI across industries. |
5. The Deep Learning Revolution (2010s)
In the 2010s, deep learning revolutionized AI by enabling machines to perform tasks with human-like accuracy.
- Neural Networks – These AI models, inspired by the human brain, process complex data in multiple layers, improving performance over time.
- Breakthroughs – Deep learning advanced image recognition, speech processing, and decision-making, making AI tools more powerful than ever.
This shift made AI smarter, leading to innovations in healthcare, finance, and automation.

AlphaGo and Advances in AI Tools
The 2010s proved that deep learning could tackle complex problems, leading to groundbreaking AI achievements.
- AlphaGo’s Victory – DeepMind’s AlphaGo defeated the world champion in Go, a game requiring intuition and strategy. This showed that AI could think creatively and make decisions beyond pre-programmed rules.
- Speech & Image Recognition – Deep learning improved AI assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa, making them better at understanding speech. Similarly, image recognition tools became highly accurate in identifying objects in photos.
These advancements pushed AI into real-world applications, making tools smarter and more intuitive.
AlphaGo: AI Mastering Complex Games
- Historic Victory – In 2016, DeepMind’s AlphaGo defeated Lee Sedol, a top Go player. Go was thought to be too complex for AI because it required intuition and strategic thinking rather than just brute-force calculations.
- Self-Learning AI – Unlike traditional AI, AlphaGo used deep learning to play millions of games against itself, continuously improving its strategy. This breakthrough proved that AI could learn, adapt, and outperform humans in highly complex decision-making tasks.
| Trend: AI Tools Demonstrating Human-Like Performance in Tasks Once Considered Too Complex for Machines |
|---|
|
This shift marked a new era where AI tools could not only analyze data but also generate creative content and make independent decisions. Some key advancements included:
|
6. Modern AI Tools (2020s–Present)
AI Tools in Daily Life:
AI has become a part of everyday life, making tasks like writing, design, and virtual assistance easier and more efficient.
- Writing Assistants – Tools like Grammarly and ChatGPT help improve grammar, style, and content generation.
- Design Tools – AI-powered platforms like Canva suggest templates, layouts, and colors, allowing non-designers to create professional visuals.
- Virtual Assistants – Smart devices like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant use AI to set reminders, answer questions, and play music.
These AI tools simplify creative tasks and enhance productivity, making advanced technology accessible to everyone.
AI’s Expanding Impact:
AI is making a significant impact across industries, improving efficiency and innovation:
- Healthcare – AI assists in diagnosing diseases, analyzing medical images, and predicting patient outcomes. It helps doctors detect conditions like cancer early for more accurate treatment.
- Education – AI-powered tools personalize learning experiences, with platforms like Duolingo helping students learn languages at their own pace and AI tutors assisting with difficult subjects.
- Business – AI automates tasks, enhances customer service through chatbots, and provides valuable data insights to help companies make better decisions.
Tip: Explore AI Tools for Free
If you’re new to AI, trying free tools can help you understand its capabilities:
- Writing – Use AI assistants like Grammarly or ChatGPT to improve grammar, refine style, and generate content.
- Design – Platforms like Canva and Fotor offer AI-powered templates, layouts, and design suggestions.
- Analysis – Tools like Google Analytics and Tableau Public help visualize and interpret data efficiently.
Experimenting with these tools is a great way to see how AI is making creative and analytical tasks easier.
| Trend: AI Tools Are Becoming More Accessible and User-Friendly |
|---|
|
AI is no longer just for experts or large companies—anyone can now use AI for work, creativity, or daily tasks.
This shift is making AI a practical tool for everyone, regardless of background or location. |
7. The Future of AI Tools (Brief Overview)
Emerging Trends:
AI’s Role in the Next Generation of Tools In the future, AI will play a bigger role in areas like robotics and autonomous systems:
- Robotics: AI-powered robots will handle tasks in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics.
- Autonomous Systems: Self-driving cars and drones, guided by AI, will change transportation and delivery services.
Example: AI-Powered Robots Transforming Industries
- Robots in factories and hospitals are becoming more efficient. For example, AI in car factories assembles parts quickly, and robots in healthcare assist in surgeries.
AI will likely assist rather than replace jobs. Many tasks will be automated, but humans will work alongside AI, focusing on tasks requiring creativity or supervision. New jobs in AI management and technology will also emerge.
| Trend: Ethical AI and Collaboration Between Humans and Machines |
|---|
|
FAQs:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) began in the mid-20th century. In 1951, Christopher Strachey developed the first AI program, a checkers (draughts) game, which ran on the Ferranti Mark I computer at the University of Manchester.
AI’s history spans several key periods:
- 1950s-1960s: Foundational work by Alan Turing and the development of early AI programs.
- 1970s: The first “AI Winter,” a period of reduced funding and interest due to unmet expectations.
- 1980s: Revival with expert systems and neural networks, leading to significant advancements.
- 2000s-Present: Rapid growth in machine learning, deep learning, and AI applications across various industries.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) aims to create machines with human-like cognitive abilities. While foundational work began in the mid-20th century, significant progress has been made in recent decades, with notable contributions from researchers like John Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton in the 1980s.
The first AI device was the Ferranti Mark I computer, which ran Christopher Strachey’s checkers program in 1951.
Alan Turing is often referred to as the father of AI due to his pioneering work in computing and the concept of machine intelligence.
Conclusion
The journey of AI tools has been incredible, evolving from simple programs like ELIZA to today’s powerful deep learning models and everyday AI applications. As we look to the future, AI will continue to transform industries, improve lives, and create exciting opportunities for innovation.
To stay updated and make the most of these advancements, stay curious and explore free ai tools for writing, design, and analysis. These tools can help simplify tasks, boost creativity, and enhance your work. The future of AI is bright, and you can be a part of this exciting journey!

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks





